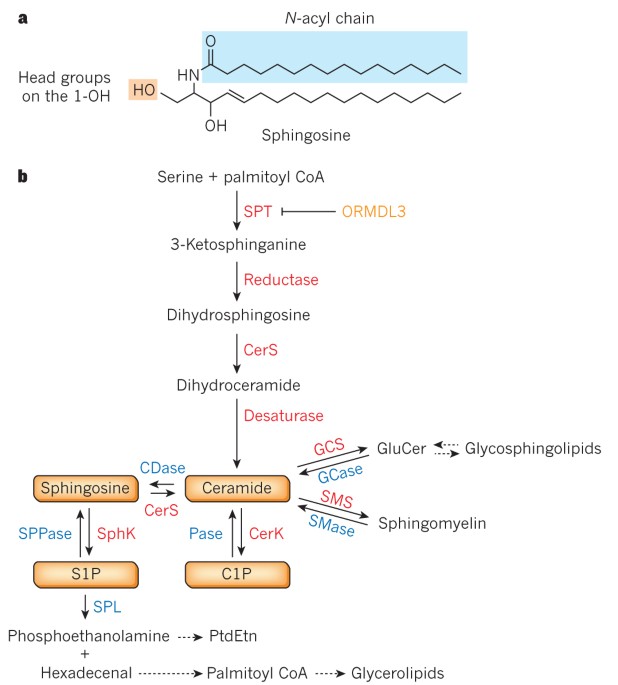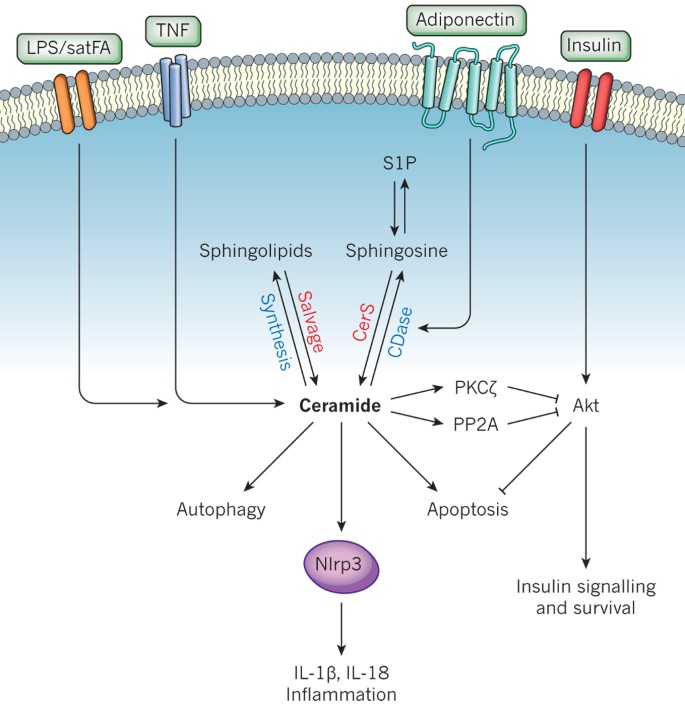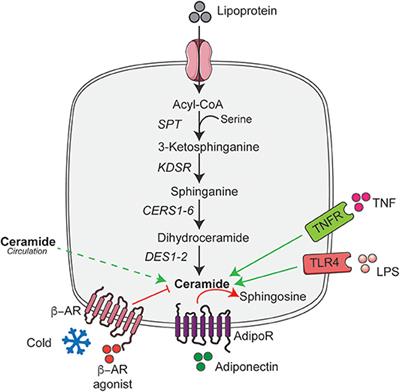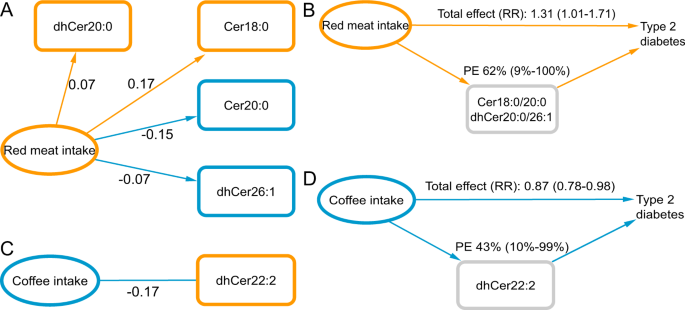
Dihydroceramide- and ceramide-profiling provides insights into human cardiometabolic disease etiology | Nature Communications

Role of ceramide in diabetes mellitus: evidence and mechanisms | Lipids in Health and Disease | Full Text
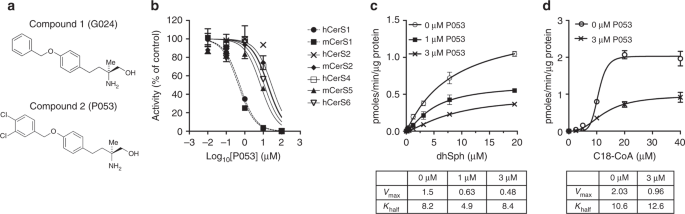
A selective inhibitor of ceramide synthase 1 reveals a novel role in fat metabolism | Nature Communications
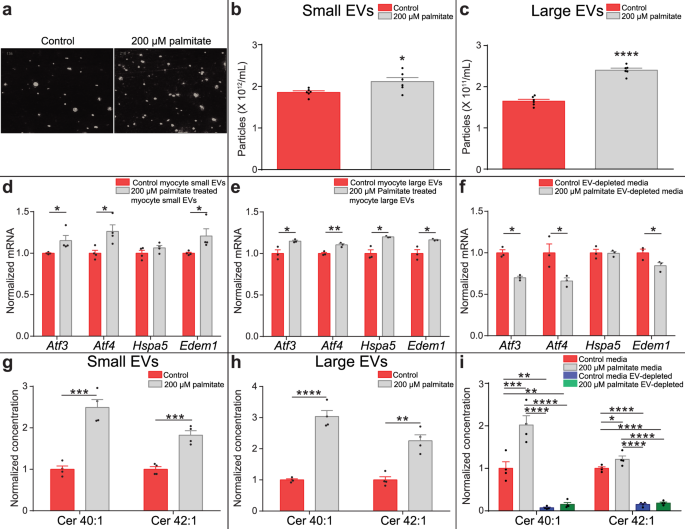
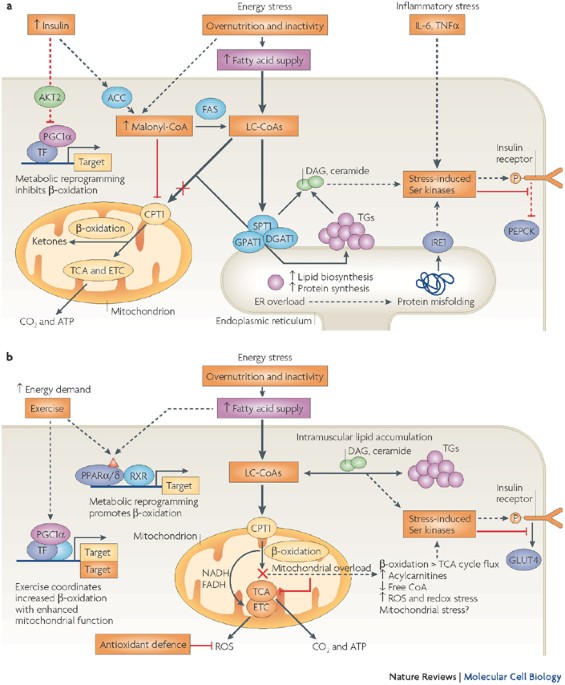
Long-chain ceramides are cell non-autonomous signals linking lipotoxicity to endoplasmic reticulum stress in skeletal muscle | Nature Communications

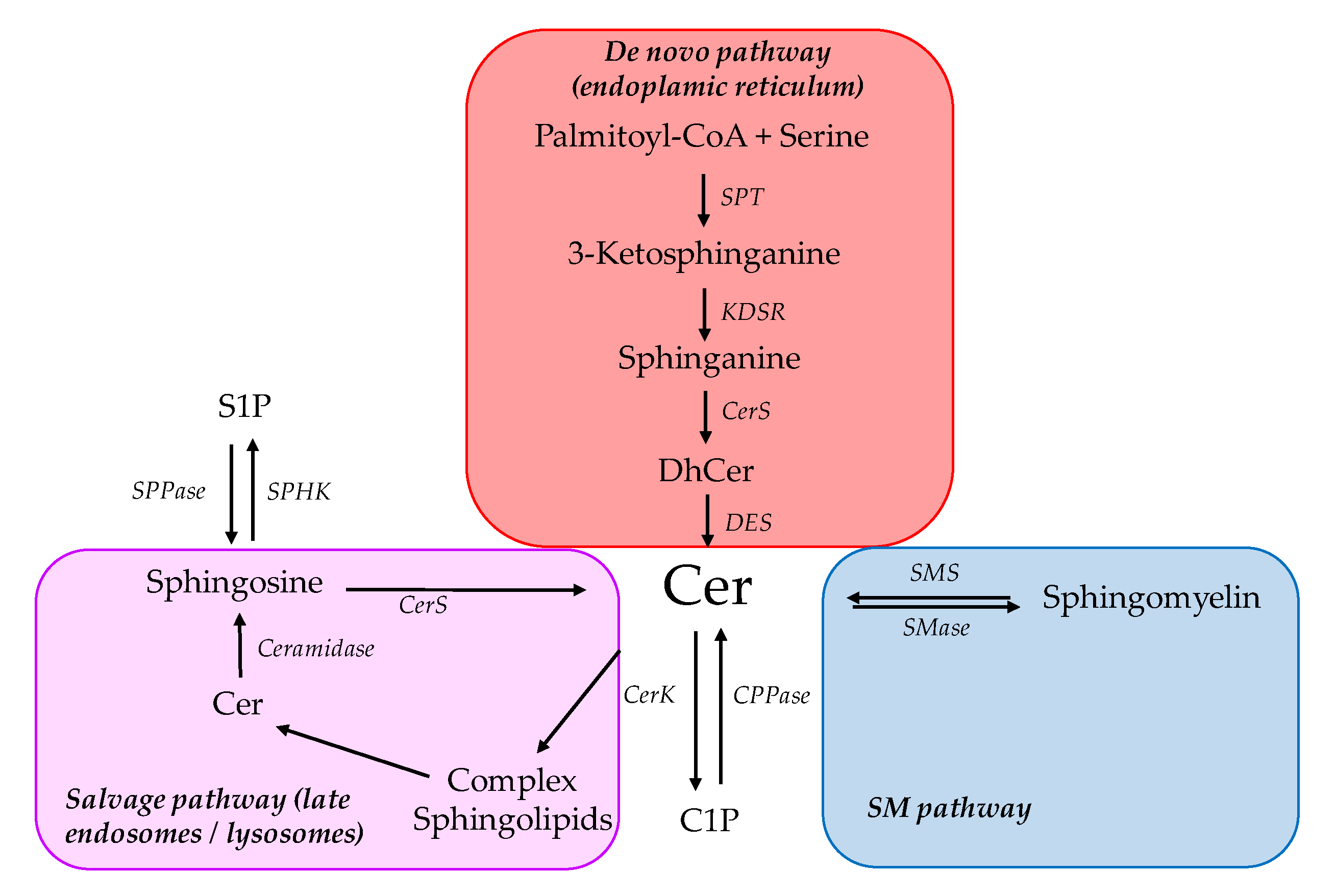
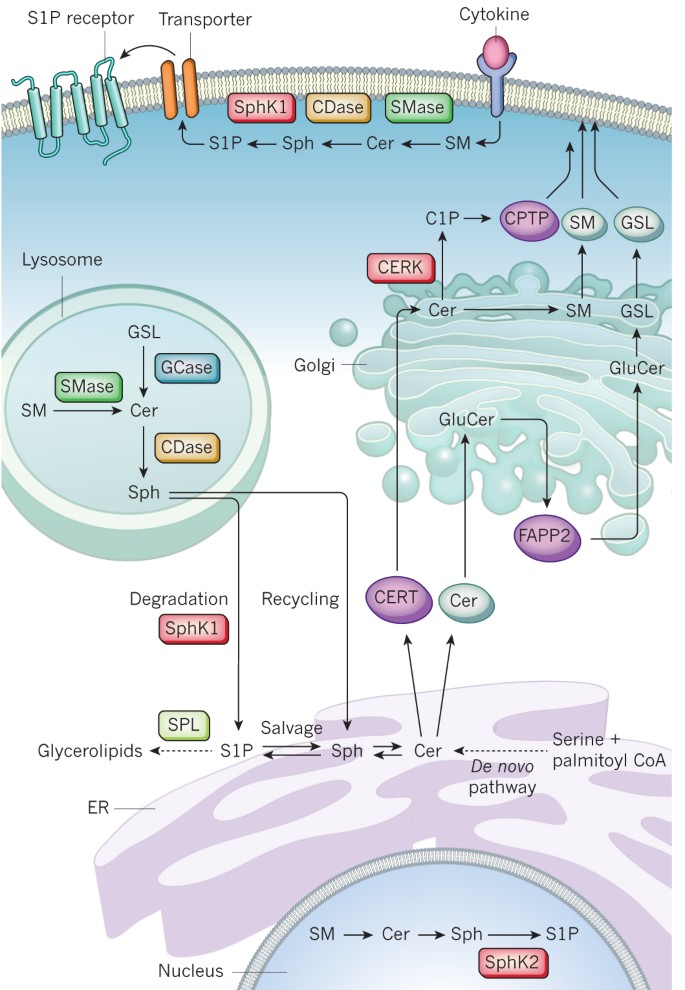
The role of ceramides in metabolic disorders: when size and localization matters | Nature Reviews Endocrinology
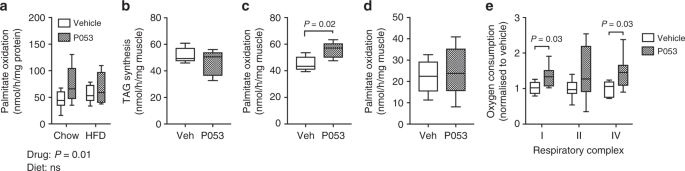
A selective inhibitor of ceramide synthase 1 reveals a novel role in fat metabolism | Nature Communications

Metabolites as regulators of insulin sensitivity and metabolism | Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology

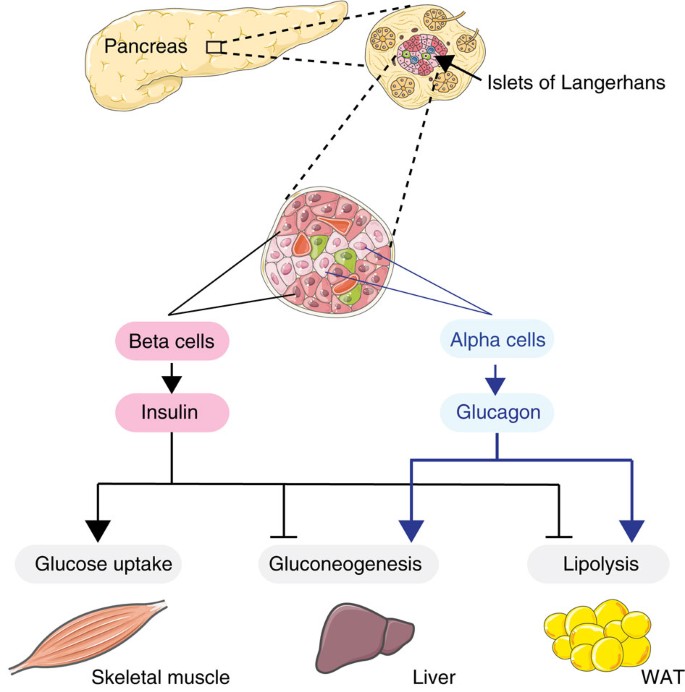
Beta-cell specific Insr deletion promotes insulin hypersecretion and improves glucose tolerance prior to global insulin resistance | Nature Communications
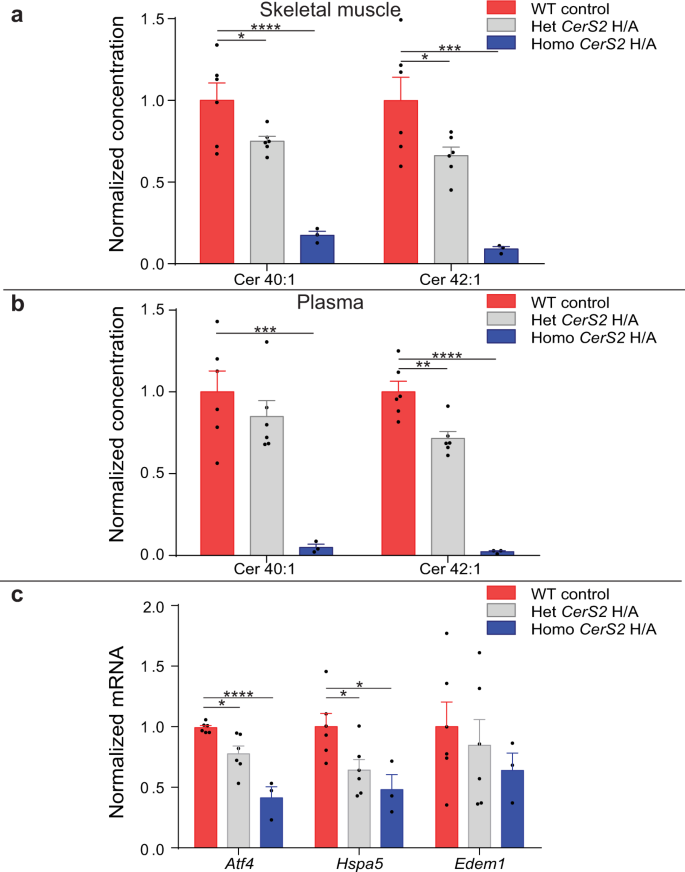
Long-chain ceramides are cell non-autonomous signals linking lipotoxicity to endoplasmic reticulum stress in skeletal muscle | Nature Communications
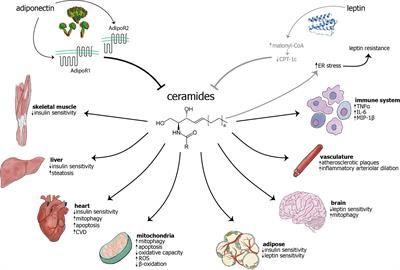
Frontiers | The Role of Ceramides in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Regulation of Ceramides by Adipokines
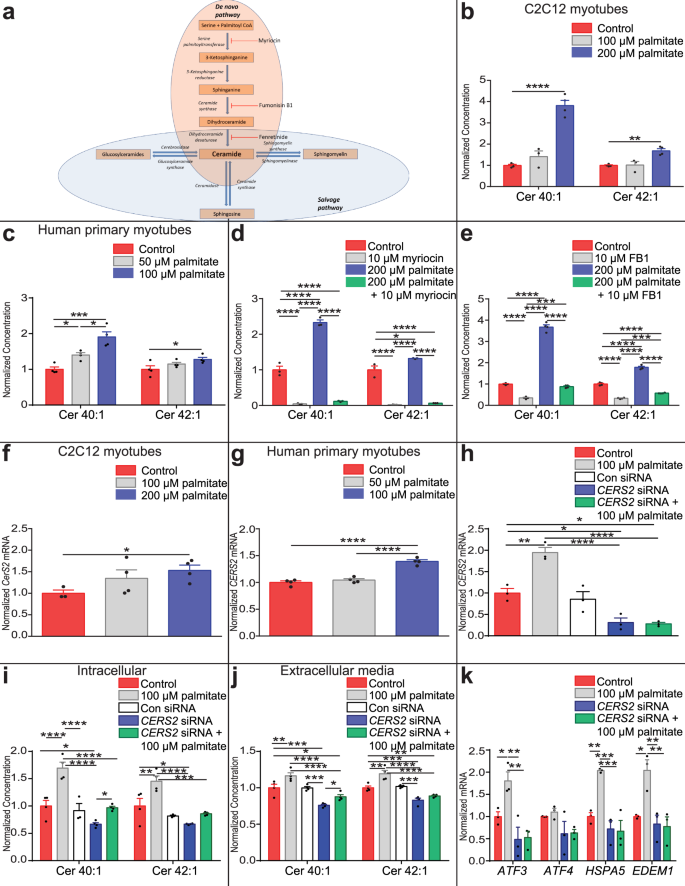
Long-chain ceramides are cell non-autonomous signals linking lipotoxicity to endoplasmic reticulum stress in skeletal muscle | Nature Communications
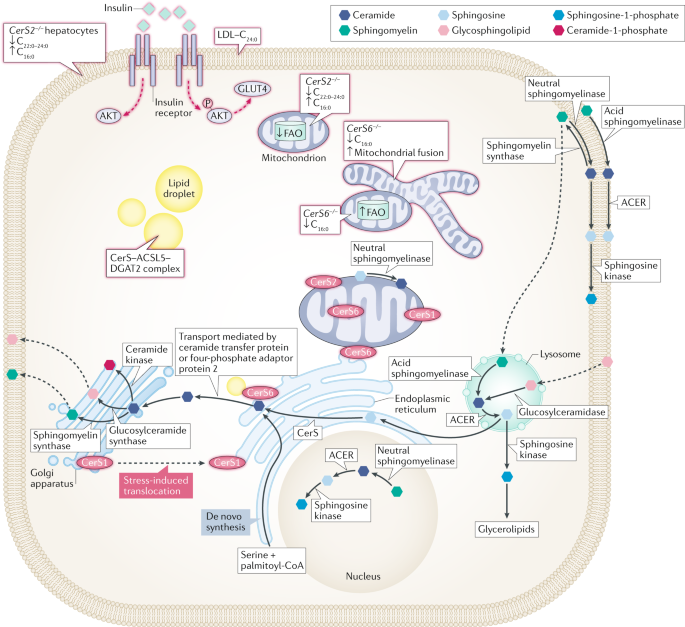
The role of ceramides in metabolic disorders: when size and localization matters | Nature Reviews Endocrinology

High-fat diet-induced upregulation of exosomal phosphatidylcholine contributes to insulin resistance | Nature Communications
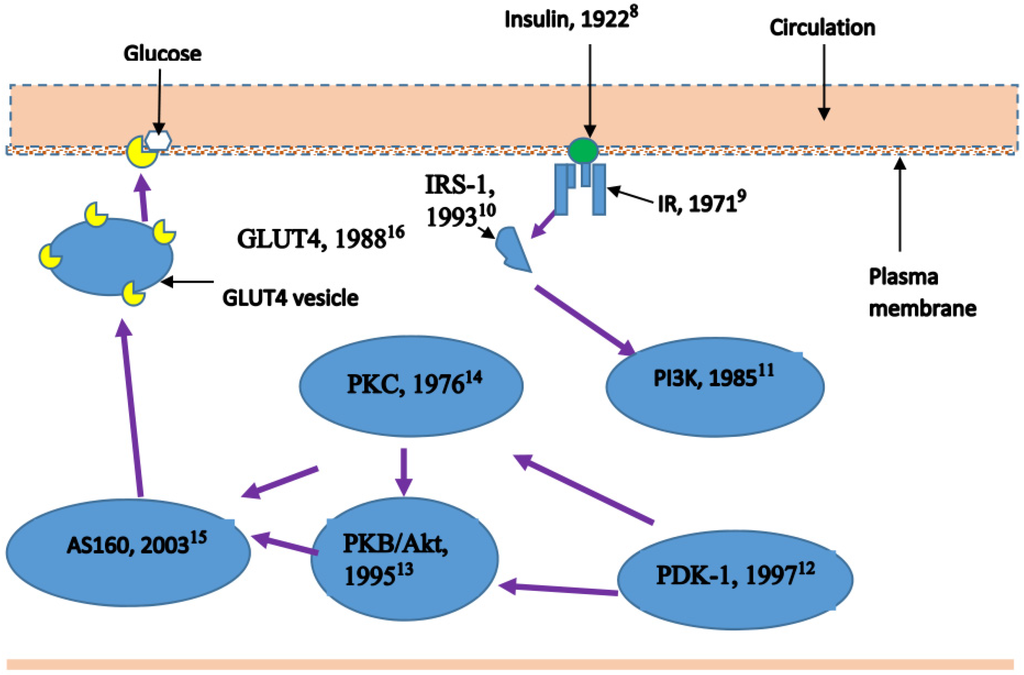
Nutrients | Free Full-Text | Lipid-Induced Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle: The Chase for the Culprit Goes from Total Intramuscular Fat to Lipid Intermediates, and Finally to Species of Lipid Intermediates
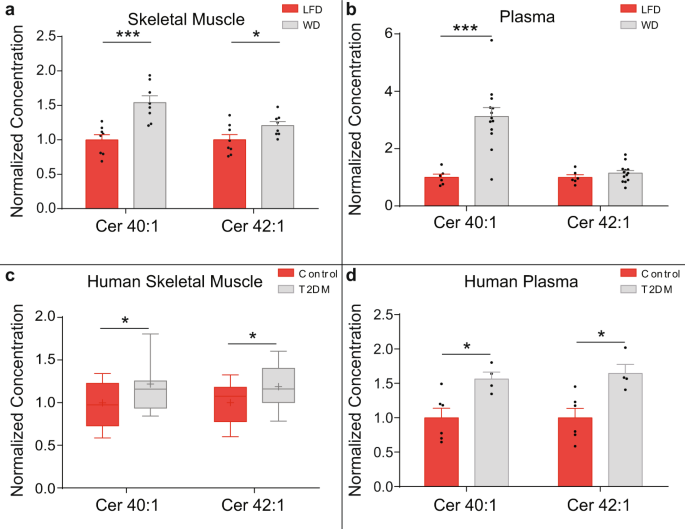
Long-chain ceramides are cell non-autonomous signals linking lipotoxicity to endoplasmic reticulum stress in skeletal muscle | Nature Communications
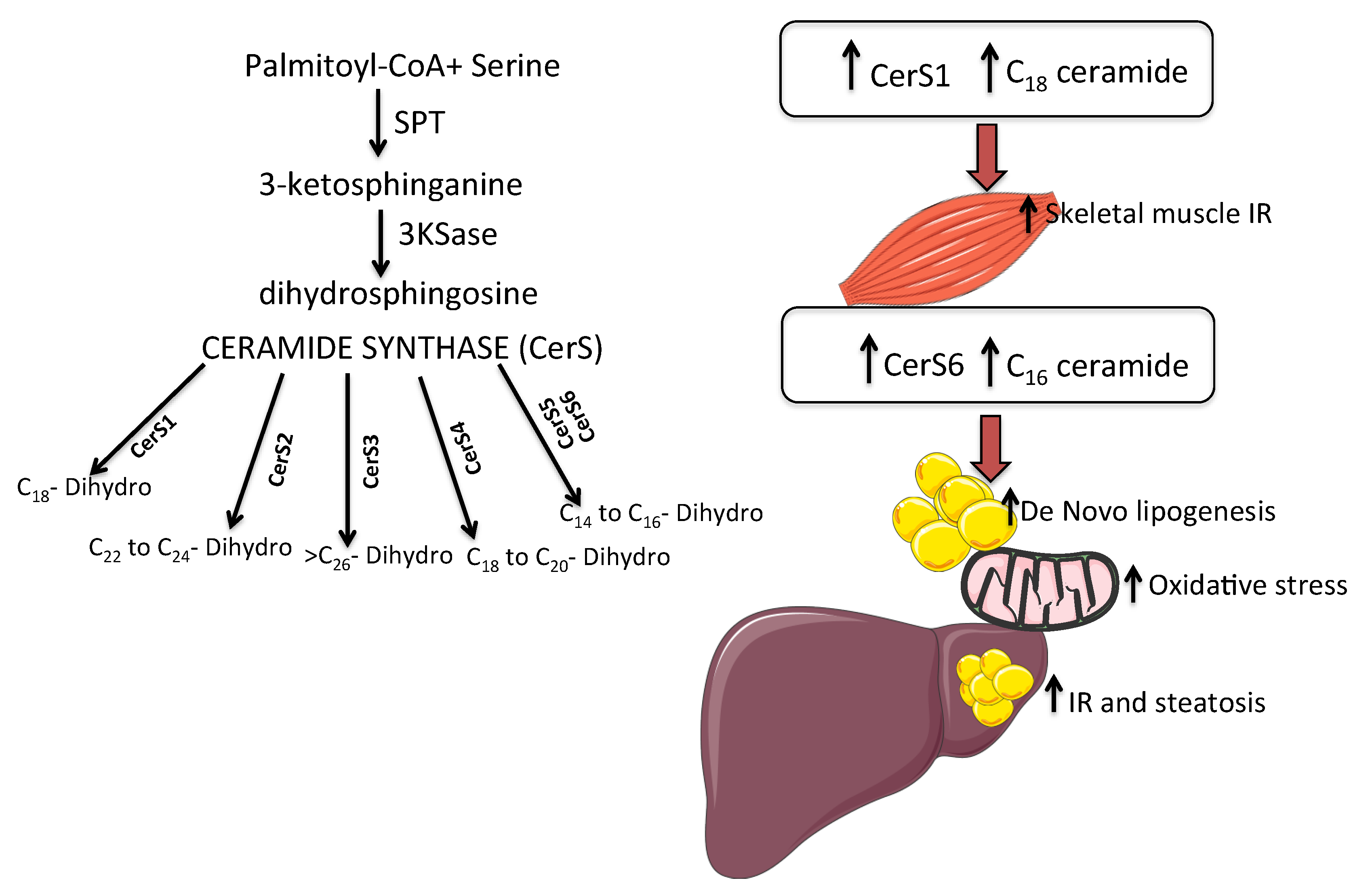
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Ceramides as Mediators of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Cardiometabolic Disease
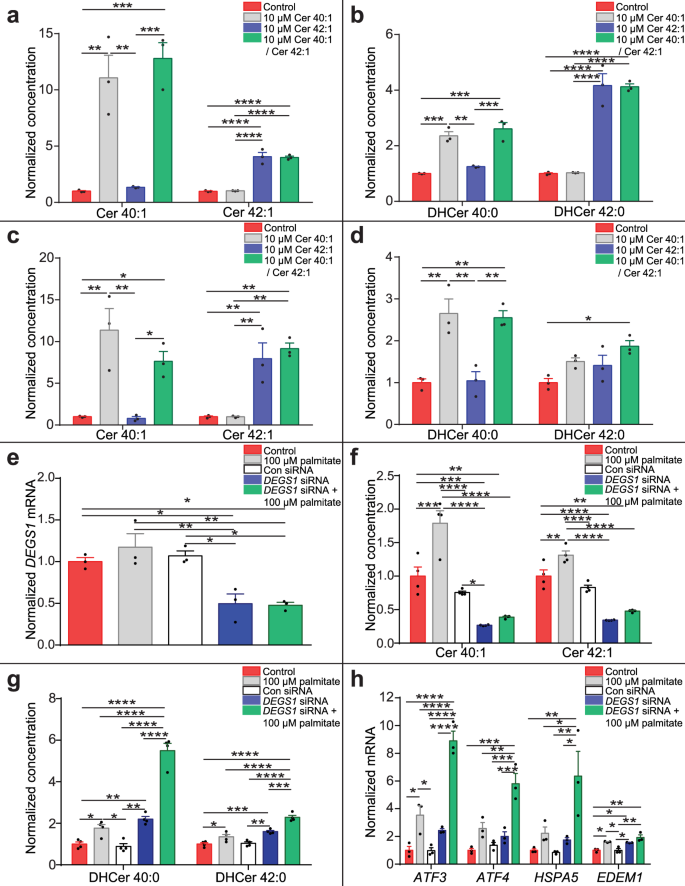
Long-chain ceramides are cell non-autonomous signals linking lipotoxicity to endoplasmic reticulum stress in skeletal muscle | Nature Communications